Turnip Moth Facts
- The simple term of Turnip Moth serves as the common name for a small but noteworthy Lepidoptera. Its scientific name, meanwhile, remains somewhat hard to pronounce. That’s because scientists know it by the official term of Agrotis segetum.
- Regardless of which term one uses to refer to it, however, most people have strong opinions about it. The first formal recognition of it as a species, meanwhile, took place in 1775. Ignaz Schiffermuller and Michael Denis hold that distinction.
- This tiny Lepidoptera also represents a particular variety of cutworm. Within most of its range of habitation, it now constitutes a threat to crops. This unfortunate fact now qualifies it as an invasive species, at least in the minds of some groups.
- For the moment, the Turnip Moth constitutes one of those rare species with a sizeable and stable population. This further holds tur throughout the entirety of its natural range. It’s also been spread to much of the world through the actions of man.
- Due to these factors, the IUCN currently has no listing for it on the organizations Red List. Certain factors could nevertheless threaten its existence in the future. Chief among these, of course, would be the dangers of habitat loss and climate change.
Related Articles
Turnip Moth Physical Description
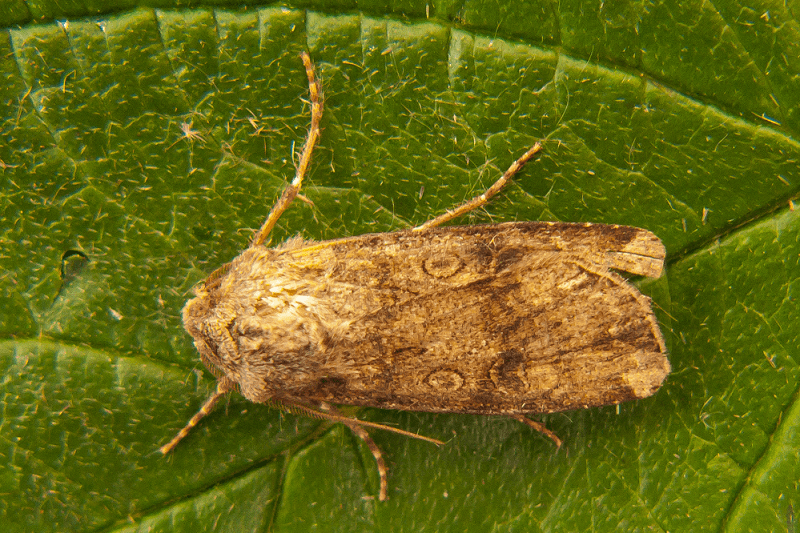
Perhaps the most notable characteristic of the Turnip Moth remains its physical description. This statement holds true due to a remarkable trait displayed by the insect. Both the size and color patterns of this arthropod vary significantly between individuals.
As a result of this, the species understandably displays comparatively extreme levels of the trait of sexual dimorphism. This fact, therefore, commonly creates confusion. It frequently leads to difficulty in telling the genders apart, even for experts.
Certain physical patterns between the sexes do remain relatively consistent, however. Among these is the fact that the females present forewings colored dark gray, brown, or black. The hindwings of this gender meanwhile, generally display as a light gray in color.
In contrast, though, the forewings of the male of the species typically present as much lighter in color. Their hindwings, on the other hand, usually develop as either whitish or light gray. This degree of difference in appearance truly sets it apart from most moths.
The other various physical attributes of the Turnip Moth, however, remain reasonably consistent with those of its kind. The body of the invertebrate, for one, averages about 0.85 in (22 mm) in length. Its wingspan, though, commonly reaches as much as 1.7 in (45 mm).
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Class: Insecta
- Order: Lepidoptera
- Family: Noctuidae
- Genus: Agrotis
- Species: A. segutum
Turnip Moth Distribution, Habitat, and Ecology
The delicate-seeming yet destructive Turnip Moth actually evolved as endemic to a wide swathe of the globe. More specifically, it developed as native to much of the continent of Europe. International commerce, however, led to its establishment elsewhere.
As a result of this, it’s now firmly entrenched in portions of both Asia and Africa as well. Wherever it appears, though, the arthropod displays an ability that further aids in its survival. That’s because it seems to be highly adaptable to a wide variety of habitat types.
Due to this clear evolutionary advantage, it frequently appears in many ecosystems. These habitats include not only farmland, parks, and gardens, but also forests, and even some areas of sand dunes. This tendency, therefore, leads it into conflict with humans.
The highly voracious larval form of the insect feeds on a wide variety of plants. In this characteristic, it clearly follows the habit of most related species. The preferred food of the creature, however, includes cotton, tomato, corn, legumes, sugar beets, and tobacco.
The larvae of the Turnip Moth further feed on the entire plant. this, in fact, extends from the leaves to the roots, thereby destroying everything. Thus, most farmers in the regions it inhabits consider it to be not only invasive, but extremely harmful, as well.
Species Sharing Its Range
Check out our other articles on 9 Bewildering African Plants, Malaysian Flying Fox, Kaieteur Falls, Dragon Moray Eel, Phallus Indusiatus, Thorny Dragon, Araripe Manakin, Orange-belted Bumblebee