Tree Heather Facts
- This variety of flora most frequently goes by the somewhat deceptive common name of the Tree Heather in parts of its native range. It does, however, possess another, less commonly used name. That’s the very similar term of the tree heath, though.
- The majority of scientific professionals, meanwhile, including researchers, usually refer to it by its technical name. That, however, is a relatively easy to pronounce term, compared to many. That’s because it bears the scientific name of the Erica arborea.
- Regardless of which term one chooses to use when referring to it, though, it remains an intriguing species. The Swedish botanist, Carl Linnaeus holds the distinction of accomplishing the first formal acknowledgment of it as a separate and distinct species.
- Though concerns exist over the size of its endemic range, it appears to be maintaining a population base that’s both sizable and sufficient. The IUCN, therefore, presently lists this marvelous work of Nature as Least Concern on its Red List of Threatened Species.
- The Tree Heather nevertheless should be considered to be facing a few threats to its existence. Loss or degradation of its habitat due to the actions of mankind pose a potential danger, of course. Its greatest threat though, comes from climate change.
Related Articles



Tree Heather Physical Description
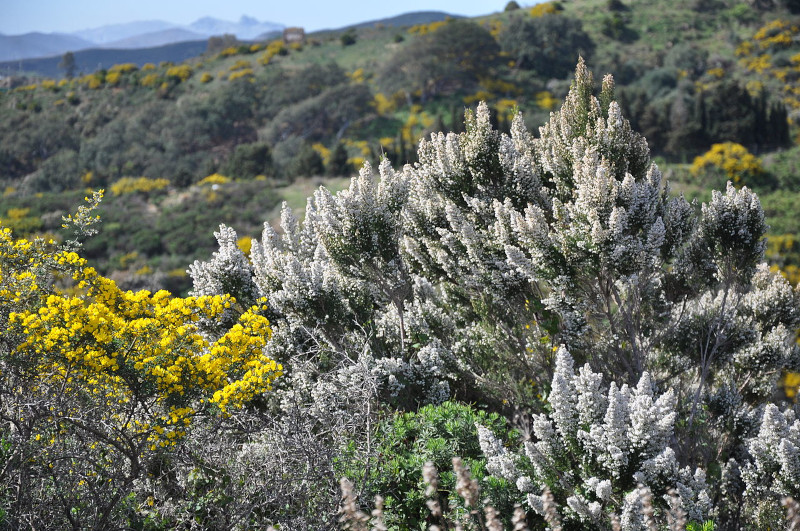
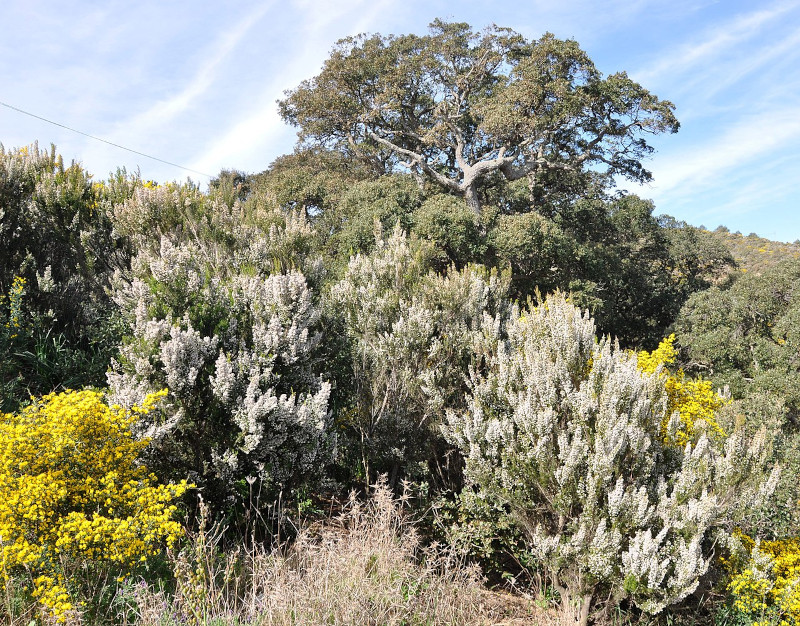
The delightful Tree Heather quickly draws the eye of all those who enocounter it. It does so, however, for several reasons, not just because of its visual appeal. That’s due to the fact that this remarkable product of evolution appears as either a shrub or small tree!
The majority of specimens develop into small-to-medium size shrubs, however. That holds true for both the wild specimens and those cultivated, typically in small gardens. In either form the plant appears in, though, the species develops as an evergreen.
Most individuals of this amazing Angiosperm reach a height ranging from 3 – 13 ft (1 – 4m). Approximately 3 – 6 ft (1 -2m), though, constitutes the most common height range. Some exceptional specimens, however, grow to heights of up to 23 ft (7m).
Each plant typically produces several, comparatively thin, upward-reaching trunks. These possess a covering of rough, brownish bark. It also produces large numbers of distinctive leaves. These further develop as long, needle-like in shape, and a dark green in color.
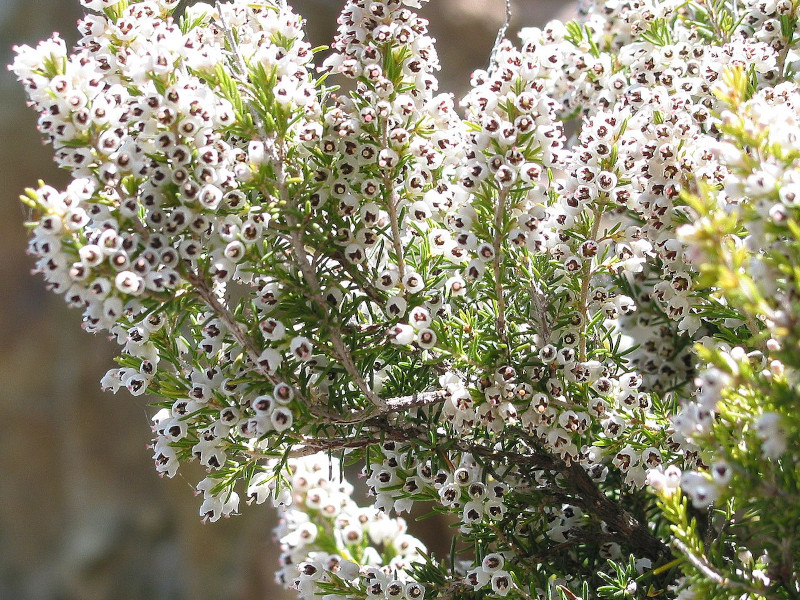
It’s the flowers of the incredible Tree Heather that understandably garner the most attention. These it produces along its many slender branches. It also produces these in huge numbers. Each further present a bright white shade, has a bell shape, and a honey-like scent.
- Kingdom: Plantae
- Phylum: Tracheophytes
- Class: Eudicots
- Order: Ericales
- Family: Ericaceae
- Genus: Erica
- Species: E. arborea
Tree Heather Distribution, Habitat, and Ecology
Unfortunately, the gorgeous Tree Heather inhabits a region of the globe that’s both limited, and highly fragmented. The reason for the fragmentation, however, currently remains unknown. Presently, it appears in widely disjunct groupings within this overall region.
More precisely, though, that zone of habitation includes the general Mediterranean Basin. This includes small parts of Asia, Africa, and Europe. From there, though, its range extends north to Bulgaria. It also grows in Portugal, and parts of the Canary Islands and Madeira.
In all the regions it does grow in, however, it displays a decided preference for several types of ecosystems. In Africa, it mainly lives in the highlands of Ethiopia, and mountains in Cameroon. Elsewhere, though, the versatile plant mainly appears in areas of shrublands.
The actions of humans, meanwhile, have caused ito become naturalized in a different part of the world as well. That’s due to the fact that, surprisingly, small populations of this wonder of evolution now appear in southeastern portions of the continent of Australia.
It’s now also become extremely popular as an ornamental plant, due to its many beautiful blooms. That further holds true both within its natural range and outside of it. Several cultivars of this natural beauty also now exist in various parts of the globe.
The Tree Heather is also highly valued for its wood. This part of the plant evolved as extremely hard, and heat resistant. It’s therefore prized in some regions for making pipes. Its tubers, roughly the size of a football, also serve as an edible component in some regions.
Species Sharing Its Range


Check out our other articles on 5 Island-Evolved Herbaceous Plants, Sculptured Mitten Lobster, Farallon Islands, Kinabalu Giant Red Leech, Nepenthes pervillei, Alaskan Timber Wolf












Leave a Reply