Madagascar’s Astounding Inhabitants continue to surprise and amaze us all with the tenacity and sheer variety of life in this rather amazing location. Furthermore, many of the different and incredible species found here exist endemically nowhere else on the planet. We sincerely hope you enjoy the information you find herein, and that it engenders an appreciation for this remote and, in some ways, still mysterious location.
Comet Moth

CCL: https://bit.ly/1ryPA8o
Comet Moth Facts
- The mesmerizing Comet Moth officially ranks as one of the largest types of silk moth known to man. To many people, it also remains one of the loveliest.
- This gorgeous Lepidoptera also displays a rather fascinating trait. The cocoons that this invertebrate spins for itself develop with numerous holes in it.
- Experts theorize this is intended to allow water to drain through, given its rather wet habitat, preventing it from drowning.
- Like many Lepidoptera, it remains wholly incapable of feeding, once it emerges from its cocoon. Therefore, its adult lifespan only measures 6-8 days.
Comet Moth Physical Description
The gorgeous Comet Moth ranks as one of the largest known types of silk moth. However, the species does display sexual dimorphism in regards to size.
The males grow larger than females. An average adult male wingspan averages roughly 8 in (20 cm). However, even larger individuals have been seen.
Meanwhile, the females remain significantly smaller, rarely attaining more than half the size of the males.
The wings also primarily display a bright yellow in color. Yet, a unique brownish-orange fringe usually appears along the outside of the wings.
In addition, lines and spots of the same darker color frequently appear on the upper side of the wings of the arthropod.
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Class: Insecta
- Order: Lepidoptera
- Family: Saturniidae
- Genus: Argema
- Species: A. mittrei

CCL: https://bit.ly/1ryPA8o
Comet Moth Distribution, Habitat, and Ecology
Unfortunately, both for humans and the Comet Moth itself, this rather breathtaking animal possesses an extremely limited habitat range.
To our knowledge, this stunning insect only lives in the rainforests of the island of Madagascar, in Africa. Furthermore, it only seems to inhabit the deepest sections.
A rather surprising mystery also surrounds the beautiful creature. It lives a primarily nocturnal life, thus its brilliant coloring serves no evolutionary purpose that scientists can determine.
In addition, each female lays between 120-170 eggs after mating, after which she quickly dies. The hatching larvae feed voraciously, primarily on only two specific species of local plants.
The combination of tiny territory range and high dependency on specific plants makes it extremely vulnerable to the threats of climate change and habitat loss.
Rosy Periwinkle
Rosy Periwinkle Facts
- Firstly, the Rosy Periwinkle forms a beautiful plant with incredible botanical usefulness. It also holds the distinction of being quite rare and endangered.
- The plant also understandably became quite popular as an ornamental plant. Despite its delicate appearance, however, it remains an extremely hardy species.
- Sadly, it also has an extremely limited endemic range. Within that range, however, it now faces the threat of loss of habitat due to the practice of slash and burn agriculture.
- Fortunately, though, this little beauty proved to be highly adaptable and successfully became naturalized in numerous other parts of the world.
Rosy Periwinkle Physical Description
The beautiful and also highly versatile Rosy Periwinkle presents itself as either a herbaceous plant or an evergreen shrub.
It also grows either vertically or runs along the ground, and sometimes attains heights of as much as 3.1 ft (1 m).
In addition, the delicate-seeming flowers of this marvelous plant appear either white with a red center or a dark pink.
The leaves typically display a glossy green in color, with a thick leathery texture.
The fruit of the Rosy Periwinkle develops as an elongated follicle, occurring in pairs. Like many plants in its family, the sap of this plant has the consistency of a thick, milky white latex.
- Kingdom: Plantae
- Phylum: Angiosperms
- Class: Eudicots
- Order: Gentianales
- Family: Apocynaceae
- Genus: Catharanthus
- Species: C. roseus
Rosy Periwinkle Distribution, Habitat, and Ecology
The incredibly lovely Rosy Periwinkle grows endemically only on the island of Madagascar, itself extremely unique.
The delicate beauty of the plant also conceals a veritable cornucopia of chemical compounds. Some of the chemicals in the Rosy Periwinkle also have high toxicity, and ingestion of even a small amount can be fatal.
However, many of the other chemical compounds within the species prove invaluable in saving lives, making it highly useful.
Some of the diseases treated by a few of its compounds include a variety of cancers, diabetes, Hodgkin’s lymphoma, and even malaria.
Madagascar Hissing Cockroach
Madagascar Hissing Cockroach Facts
- The rather fascinating, if repugnant to many, Madagascar Hissing Cockroach ranks as one of the largest known species of the cockroach on earth.
- It also might surprise many of our readers to learn that within its native range, many people keep specimens of this invertebrate, and related species, as pets.
- Yet, perhaps the most astounding thing about this particular cockroach, in the minds of many people, remains the fact that it actually makes an easily audible hissing sound, as its name suggests.
- Due to its rather great size, and unique attributes, the species has often been used in Hollywood movies.
Madagascar Hissing Cockroach Physical Description
Mature adult specimens of the rather remarkable Madagascar Hissing Cockroach remain capable of reaching a total length of up to 3 in (7.5 cm).
Also unlike most other species of cockroach, this particular invertebrate remains entirely wingless. It is, however, an excellent climber, and even appears capable of climbing smooth glass. Imagine that.
This creature does display a mild degree of sexual dimorphismm. In this case, males develop significantly thicker and hairier antennae, as well as horn-like projections on the thorax.
The coloring is a rather common combination of reddish-brown and black.
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Class: Insecta
- Order: Blattodea
- Family: Blaberidae
- Genus: Gromphadorina
- Species: G. portentosa
Madagascar Hissing Cockroach Distribution, Habitat, and Ecology
As its common name implies, the Madagascar Hissing Cockroach evolved as endemic only to the island of Madagascar in Africa. This remains a highly isolated location, even today.
Its native environment consists of the dense jungle regions of the island. Also, within that environment, it most commonly inhabits rotting logs.
Further, the name of this cockroach derives from its ability to force air through its breathing spicules forcefully. In fact, while there are numerous other insect species that make such a sound, the Madagascar Hissing Cockroach is the only insect humans know of to make noises in this particular manner.
The species also actually possesses three distinctly different hissing sounds.
One solely the males use for attracting females. Another – when they are startled. The third serves during combat.
Finally, it feeds primarily on decaying vegetable matter and also possesses a lifespan of as much as 5 years.
Fossa

CCL: http://bit.ly/2xLZ0ap
Fossa Facts
- The Fossa constitutes a unique animal. Individuals actually combine many of the physical traits of civets, felines, and mongooses
- Rather surprisingly, its scientific name means hidden anus (from Greek).
- Cryptoprocta ferox lives only on the island of Madagascar. It remains secretive by nature and has not been widely studied.
- The IUCN lists the animal as Vulnerable due to the combination of its highly restricted zone of habitation and, unfortunately, the ongoing devastation of its native habitat.
Fossa Physical Description
The Fossa is so unique that it actually has flexible ankles. Along with its partially retractable claws, this enables the creature to climb headfirst down trees.
The mammal attains an average body length of about 31 in (80 cm), and a weight of about 19 lb (8.6 kg). The tail sometimes grows nearly as long as the body.
Check out other animals with very long tails: Snow Leopard and Asian Palm Civet.
The Fossa does display sexual dimorphismm, with the males being larger than the females.
Its coloring predominantly includes light to dark brown on the back and sides, and a creamy white on the underbelly. The head develops tapered, and the ears grow relatively large.
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Carnivora
- Family: Eupleridae
- Genus: Cryptoprocta
- Species: C. ferox
Fossa Distribution, Habitat, and Ecology
The Amazing Fossa remains especially adapted to forest environments, so lives only in remaining forest regions on Madagascar. It prefers either deciduous forests or areas of tropical rainforest.
The animal evolved as carnivorous in nature, and generally cathermal in its habits, hunting by both day and night.
Rather surprisingly, it ranks as the top predator in Madagascar and its diet consists largely of lemurs. Individuals will, however, take other prey opportunistically.
The Fossa primarily lives as a typically a solitary creature, except when rearing young.
It communicates with other fossas primarily through scent glands, but also makes different sounds like meowing, yowling, and sighing.
The female experiences a unique transformation during puberty: she becomes temporarily masculine, a trait popular as transient masculinization. The features are then reversed.
Its lifespan in the wild remains unknown though captive individuals live as much as 20 years.
Coconut Crab
Coconut Crab Facts
- The Coconut Crab is an extremely large species of terrestrial hermit crab. In fact, this animal remains the largest known land-dwelling arthropod on Earth.
- Further, the Coconut Crab has evolved a number of adaptations for a land-based life. The young use the discarded shells of gastropods for shelter.
- The adults develop a sturdy exoskeleton and possess primitive lungs, instead of gills. These cannot swim, and quickly drown if submerged.
- In addition to all these facts, this amazing creature has actually learned how to use its powerful claws to climb trees.
Coconut Crab Physical Description
The Coconut Crab attains a body length of as much as 16 in (40 cm). In addition, its leg span reaches as much as 3 ft (0.91 cm) while large specimens may weigh as much as 9 lb (41. kg). On average, the females grow slightly smaller than the males.
The animal also possesses 10 legs, with each pair of legs evolved to serve a specific purpose. The first pair is the large, powerful pincers which serve for combat and acquiring food.
The next two pairs are for climbing and walking, while the fourth pair is smaller and the young use them to retain the protective shell they acquire. In adults, these assist in walking.
The last pair is commonly kept inside the shell. Males utilize them in mating, while females use them to care for their eggs.
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Class: Malacostraca
- Order: Decapoda
- Family: Coenobitidae
- Genus: Birgus
- Species: B. latro
Coconut Crab Distribution, Habitat, and Ecology
The rather incredible Coconut Crab evolved as native to bodies of land in the Indian Ocean and portions of the Pacific Ocean.
Its range of habitation extends from Zanzibar to the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn. The Coconut Crab has also inhabited the mainlands of Madagascar and Australia.
In addition, the largest known concentration of this species is on Christmas Island, in the Indian Ocean. In the Pacific Ocean, it lives in multiple locations which include the Cook Islands, the Line Islands, and the Gambier Islands.
The crabs have also evolved an extremely keen sense of smell. Individuals feed primarily on nuts, seeds, and fruit. It will, however, feed on carrion when it is available.
Seychelles Sheath-Tailed Bat
Seychelles Sheath-Tailed Bat Facts
- The rather fascinating small Seychelles Sheath-Tailed Bat proves size remains irrelevant. It currently officially ranks as the fifth rarest creature on earth.
- Bats of all kinds classify as mammals of the family Chiroptera. These remarkable creatures remain the only known mammals capable of true flight.
- Its common name derives from the presence of a small membrane extending between the hind legs that can be placed over the tail.
- Sadly, this interesting species now only inhabits a severely restricted habitat range. This makes the animal extremely vulnerable.
- The greatest threats to its continued existence as a species appear to be continued loss of habitat to the planting of coconut plantations, as well as the presence of invasive species.
- Experts place its numbers at fewer than 100 remaining individuals. The IUCN appropriately currently lists the harassed creature as Critically Endangered.
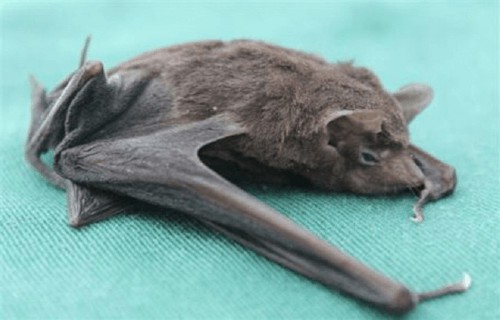
Seychelles Sheath-Tailed Bat Physical Description
Firstly, the extremely rare and threatened Seychelles Sheath-Tailed Bat evolved as a rather diminutive member of its order. An average head and body length totals between (2.1 – 2.5 in) 55 – 65 mm.
Also, a slight degree of sexual dimorphism occurs in the species, in regards to weight. Males typically weigh about 10% lighter than the slightly thick-bodied females.
In coloring, a deep reddish-brown to black also predominates on the wings and back of the body. However, the underside of the body generally presents shades of gray or lighter shades of brown.
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Chiroptera
- Family: Emballonuridae
- Genus: Coleura
- Species: C. seychellensis
Seychelles Sheath-Tailed Bat Distribution, Habitat, and Ecology
The terribly threatened Seychelles Sheath-Tailed Bat now exists only in the Seychelles Islands, north of Madagascar in the Indian Ocean, near Africaa.
Perhaps it also once throve in great numbers in the region, but it now exists only in a few locations. This species generally roosts in small caves and the cracks and crevices of rock faces.
In addition, unlike many types of bats, which typically roost in enormous groupings, it forms harem colonies generally comprising 1 or 2 males and multiple females.
Like many endangered animal species, the principal culprit in its population decline is also habitat deterioration due to the influx of non-native plant species.
Many of the native insect species cannot feed upon these invasive species of plants, and their own numbers have therefore greatly decreased.
This, in turn, has the obvious effect of significantly reducing the available food source for the bats, since the species has an entirely insectivorous diet.
Kalanchoe

CCL: http://bit.ly/2IwGIlo
Kalanchoe Facts
- Firstly, Kalanchoe serves as the name for an extensive genus of roughly 125 known species of tropical, flowering succulents.
- In addition, despite its great range, only one recognized species of this genus evolved as endemic to the New World, however.
- People also cultivate Kalanchoe quite often as rock garden plants, or as household plants. The plant’s varieties are popular for a variety of reasons.
- Finally, in 1763, the botanist Michel Adanson was the first to describe the genus.
Kalanchoe Physical Description
Most forms of Kalanchoe evolved as either perennial herbaceous plants or shrubs. However, a few species remain either annual or biennial in nature.
Also, some of the largest varieties may sometimes attain a height of as much as 20 ft (6 m). Most varieties of the plant, however, remain less than 3 ft (1 m) in height.
The plants are rather distinctive in how the flowers grow. The plant produces new cells on the inner surfaces of the petals which force them outward.
These will also grow them on the outside of the petals to force them closed.
- Kingdom: Plantae
- Phylum: Angiosperms
- Class: Eudicots
- Order: Saxifragales
- Family: Crassulaceae
- Genus: Kalanchoe

Kalanchoe Distribution, Habitat, and Ecology
The many various species of the amazing Kalanchoe principally developed as native to the regions of Africa, Europe, and Asia.
A total of 56 remain species evolved as native to Africa, and another 60 species to Madagascar. The plant also appears to be especially present in China, in Southeast Asia.
The genus also remains quite well known for many attributes that make it attractive to horticulturists.
These include ease of propagation, low water requirements, an displaying a rather wide variety of colors among the blooms.
Furthermore, a few varieties of Kalanchoe reproduce asexually, and at least one species of is an air plant and thus reproduces vegetatively.
Many species are also popular food sources for the caterpillar form of the Red Pierrot Butterfly. Many are also toxic, while others have been ingredients in traditional medicines.
Lowland Streaked Tenrec

CCL: https://bit.ly/2DuliCV
Lowland Streaked Tenrec Facts
- The bizarre-looking Lowland Streaked Tenrec forms an extraordinarily unique species of Tenrec. The species has also developed several completely unique attributes
- Remarkably, it remains the only known mammal to generate sound by stridulation. Mothers use this as a means of communicating with their young.
- Also, it serves as the only known species of tenrec to be active by both day and night. All other tenrecs only become active at night. This serves to give them a competitive edge.
- Lastly, this ranks as the only known tenrec to live in groups. It also tends to remain with its family, living in groups of as many as twenty individuals.

CCL: https://bit.ly/2DuliCV
Lowland Streaked Tenrec Physical Description
The Lowland Streaked Tenrec forms a rather diminutive animal. Mature adults attain an average length of head and body of about 6.5 in (16.5 cm). It also stays quite light, rarely exceeding 7 oz (200 grams) in weight.
Its snout grows rather elongated, while the tail appears vestigial. The head, back, and sides appear black, with long yellow stripes. The underbelly typically displays a chestnut brown and covered with soft fur.
Yet the rest of the body is covered with numerous long, sharp quills. It is also important to note that some of these develop as barbed and detachable, and used in defense.
In fact, these seem most numerous on the crown of the head. Also, it is the remarkable quills that are used for stridulation.
The Lowland Streaked Tenrec rubs these together to generate a unique sound. This sound is so low-pitched that it is below the threshold of human hearing.
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Afrosoricida
- Family: Tenricidae
- Genus: Heminecentetes
Lowland Streaked Tenrec Distribution, Habitat, and Ecology
The Lowland Streaked Tenrec inhabits a rather limited range. The species is found throughout less than half of the island of Madagascar, near Africaa. Its range consists almost entirely of lowland (hence the name) tropical rainforest.
Consequently, in the loose soil, it typically constructs long, shallow burrows in which to dwell. These are also rarely more than 6 in (15 cm) beneath the surface.
The species is primarily insectivorous, but will also consume worms and fruit.
Its principal predators include the Fossa and the Malagasy Mongoose. Attacking the nose and paws of a predator with the quills is its only defensive strategy.
Breeding usually occurs between October and December. An average litter consists of 5-8 young.
Sadly, its lifespan remains short, averaging less than 2.5 years.

CCL: http://bit.ly/2IwGIlo
Madagascar’s Astounding Inhabitants
We hope you have enjoyed reading this article about Madagascar’s Astounding Inhabitants as much as we enjoyed writing it. This is such an unbelievable location, it must be experienced inn person to be believed. But, as is true of most places in the world today, many of these very forms of life find themselves in mortal peril. we must do all we can to protect them.
Check out our other articles on 10 Dazzling Denizens of the Depths, 5 Rare Mind-Blowing Cloud Types, 8 Swoon-Worthy Caves, 7 Breathtaking Beaches of the World






















Leave a Reply