Elephant Beetle Facts
- First of all, Elephant Beetle forms the common name of a particular species of the scarab beetle. Furthermore, only 3 known subspecies of this rather impressive and extremely large and powerful insect currently exist.
- In addition, all currently known varieties of the remarkable invertebrate appear to have evolved as Neotropical creatures. The larval form of this enormous insect takes an astonishingly long time, for an insect, at least, to mature into adult individuals.
- In a hard-to-believe occurrence, it once served as the focus of an experiment sponsored by the Pentagon, in Washington, DC, in the United States. The experimented investigated the possibility of controlling its larval form remotely.
- Quite fortunately, unlike many related species, its numbers appear to be sufficient and stable across its endemic range. Therefore, the IUCN presently lists it as Least Concern. However, it nevertheless faces the potential threat of climate change, like all creatures on the earth.
Related Articles
Elephant Beetle Physical Description
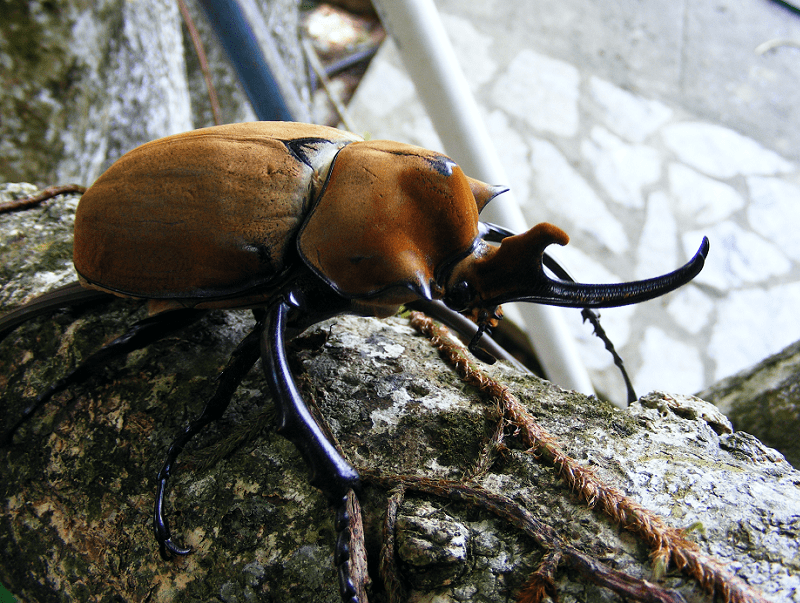
Firstly, the truly amazing Elephant Beetle presents a rather significant degree of sexual dimorphism. In this instance, this natural principle displays itself in two ways. One of these happens to be in the variation of physical size between the genders.
Secondly, this holds true due to the fact that the males of this species attain an enormous size in relation to the females. That’s because males achieve average lengths of as much as 4.75 in (12 cm). Meanwhile, females only average about 1.6 in (4.1 cm).
But, yet another form of sexual dimorphism makes itself known in this arthropod in terms of physical appearance. This occurs due to the fact that the males possess two large horns. Yet, the smaller females of this fascinating species display no horns at all.
Finally, the legs and body of this giant among insects typically appear as black in color. However, the exoskeleton of the Elephant Beetle remains covered with a rather think layer of fine hairs. These serve as the source of its often-perceived yellowish-brown color.
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Class: Insecta
- Order: Coleoptera
- Family: Scarabaeidae
- Genus: Megasoma
- Species: M. elephas
Elephant Beetle Distribution, Habitat, and Ecology
Most notably, the amazing Elephant Beetle appears to be endemic to portions of Australia, Mexico, Central America, and South America. Within that territory range, it most commonly inhabits regions of rainforest. This remains especially true of the mighty Amazon rainforest.
Normally, this creature, both the adult and larval forms, inhabits virtually all portions of this region. However, deforestation has greatly reduced its available habitat. But, where possible, it still attempts to survive in areas of the heavy foliage typical of such regions.
In addition, the larvae of this astonishing insect primarily occur in large, decaying logs. Quite surprisingly, though, these sometimes take as long as 3 entire years to mature into adults. During this time, the individual specimens feed rather voraciously on the decaying wood.
Finally, the average lifespan of an adult Elephant Beetle only measures between 1 – 3 months. Thus, it spends the majority of its life as a larva. The adults prefer to feed on the sap of particular trees, as well as various fruits and tree bark. It also lives a primarily nocturnal life.
Species Sharing Its Range
Check out our other articles on 7 Outstanding Flightless Birds of the World, Mountain Chicken, Hot Water Beach, Monkey Puzzle Tree, Diving Bell Spider, Clymene Dolphin, Earth’s 7 Mightiest Rivers