
Aye-aye Facts
- The surprisingly short, yet still quite distinctive, term of Aye-aye serves as the most typically used moniker for this remarkable mammal. In fact, it’s presently the only broadly accepted common name for the creature. While not unknown, that’s somewhat uncommon.
- Within scientific circles, however, the amazing animal is perhaps much better known to the majority by its technical appellation. Unfortunately for the layperson, though, that’s an extremely difficult label to pronounce, even compared to most other such epithets.
- That’s because this intriguing creation of Nature and evolution holds the tag Daubentonia madagascariensis. It received that honorific due to the efforts of Johann Friedrich Gmelin. The German naturalist recorded the first recognition of it as a fully distinct species.
- Regardless of which of these one chooses to use when speaking of it, the small creature remains a surprising animal. It currrently represents the only known surviving member of both its Family and Genus. Another species in that group went extinct less than 1,000 years ago.
- Regrettably, the remarkable Aye-aye holds a truly precarious position regarding its population in the wild. This seems to be quite small, and easily disturbed. Accordingly, the IUCN now lists the marvel of Nature as Endangered on its published Red List of Threatened Species.
- The fascinating animal now faces multiple threats to its continued existence. Most of these stem from the actions of humans. Due to superstitions, locals often kill them on sight. Deforestation, due to human actions, and climate change also continue to endanger it.
Related Articles
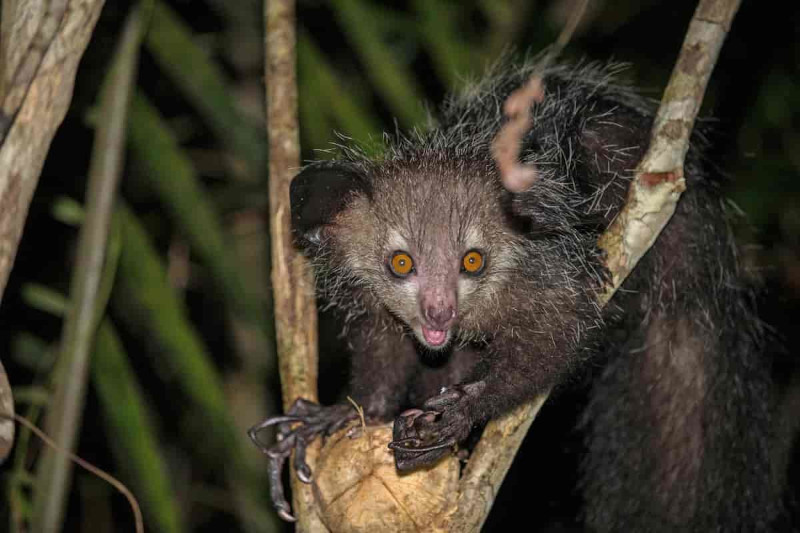




Aye-aye Physical Description
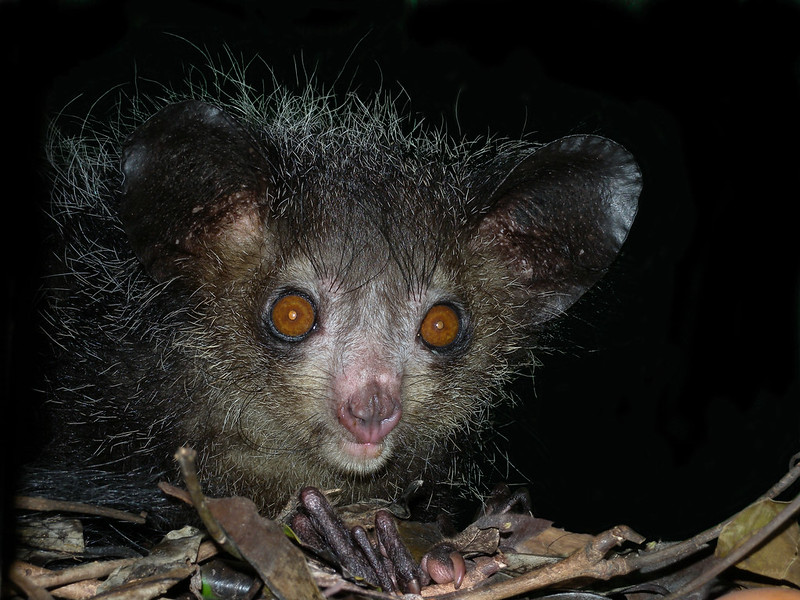
The unusual Aye-aye almost always captivates those fortunate enough to encounter it in the wild. Though few find it visually appealing, it nonetheless captures one’s attention. It does not do so, though, due to impressive physical stature. That’s true since it’s a physically small species.
In terms of both size and appearance, it follows a pattern prevalent among all known varieties of lemurs. That’s manifested by the fact that it displays no notable degree of the physiological characteristic of sexual dimorphism. The genders therefore appear virtually indistinguishable.
A fully mature individual of this mammal attains an average head and body length measuring approximately 14 – 17 in (36 – 43 cm). The lengthy tail, though, significantly increases the total size. This distinctive appendage reaches a mean growth of 22 – 24 in (56 – 61 cm) itself.
The biological wonder of evolution also achieves similarly diminutive qualities in terms of its weight. The same mature adult specimens reach an average mass equaling only about 4 lbs (1.8 kg). As a result, the overall body shape thus tends to be relatively thin and elongated in structure.
In its youth, the awesome animal presents a significantly different pattern of coloring than mature adults. At this time, the underside of the body shows varying shades of a deep, dark brown. Yet, the upper part of the body usually shows a brilliant silvery shade, with a dark stripe down the back.
As it matures, though, this pattern among examples of the Aye-aye changes. It typically becomes a full-body coverage of dark fur, though it includes random hues. Most tend to consist of dark shades of yellow or brown. On the heqad and back, however, the tips of the hair shows white.
Yet, it’s the hands of the creature that typically garner the most attention from viewers. That’s due to the nature of its distinctive fingers. All of these develop as quite bony in nature, but the third stands out. This digit develops as much longer and thinner than the others on each of its hands.
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Primates
- Family: Daubentoniidae
- Genus: Daubentonia
- Species: D. madagascariensis

Aye-aye Distribution, Habitat, and Ecology
The fabulous, if admittedly unusual, Aye-aye evolved as native to a very small section of the surface of the earth. This location probably won’t surprise many who learn of it, however. That’s because Nature created this biological marvel as endemic to only a single location in the world.
That’s the mesmerizing island of Madagascar, itself an astonishing natural wonder. Situated off the east coast of Africa, it’s a setting filled with a myriad of marvels. Yet, even within this highly limited zone of habitation, it primarily appears in specific portions of the eastern coast of the island.
Thankfully, the unusual creature also evolved a moderately extensive degree of flexibility in terms of its habitat choices. Due to this extreme adaptability, it appears in several separate types of ecosystems. The majority of individuals, though, live in either rainforest or deciduous forests.
Those individuals living in the rainforest spend the largest part of their time in the dense canopy. As a result, most of these are seen at altitudes of roughly 230 ft (70 m). Sadly, however, many are now forced to take up residence in cultivated areas, due to ongoing deforestation in their region.
The Aye-aye also lives as mostly nocturnal in nature, and almost exclusively arboreal, as well. It spends the vast majority of its life high in the tree tops. There, it carries out its activities, such as mating, eating, and sleeping. It does the latter in large nests it builds among the branches.
The animal also lives a principally solitary life, generally with the only exception being for mating purposes. This activity occurs throughout the year. Females generally give birth to one live offpring every 2 -3 years. The young typically remain in the nest for 2 – 3 months, before leaving.
The creature further evolved as omnivorous in both its dietary needs and preferences. The great majority of its typical diet consists of such fare as fruits, nuts, and seeds. Yet, the animal also consumes nectar, honey, fungi, and insects. In turn, its only known predator consists of the Fossa.
Species Sharing Its Range


Check out our other articles on 3 Surprising South American Moths, Cape Porcupine, Southern Darwin’s Frog, Great Barrier Reef, Cheddar Pink, Agile Ground Mantis, Rough-nosed Horned-Lizard









Leave a Reply